An instant-on PC is something that’s too good to be true, especially for a Windows 10 computer, which takes quite some time to boot up. So, Microsoft introduced a feature - Fast Startup - in Windows 10 and took a shot at reducing the startup time.
For many users, enabling Fast Startup in Windows 10 panned out really well. The boot time was brought down to less than 10 seconds. It also sped up the POST (power-on-self-test) routine and made system reboot quicker.
But, that’s not all there is to the Fast Startup feature. So, let’s throw some light on this tool and learn more on Fast Startup in Windows 10.
Fast Startup on Windows 10 - Explained
The built-in tool was first introduced in Windows 8, and then carried on to Windows 10. So, what is Fast Startup? It is a feature that provides faster boot time on Windows PCs.
When a Windows computer is booting up, there are dozens of processes running in the background and being tested for reliability. Many of these processes have nothing to do with the system startup. So, the Fast Startup skips over such files and processes , and therefore, the boot time reduces.
The Fast Startup feature also momentarily disables a few services during the boot up time. It can temporarily put a hold on high-processing Microsoft services and third-party softwares to boost Windows 10 startup.
-
How is Fast startup different from Hibernate?
Some technical definitions dub Fast Startup as a hybrid state where your Windows system shuts down and hibernates at the same time. There’s truth to that, but Fast Startup is still quite different from the Windows Hibernate mode.
When your Windows 10 is in hibernation, the last state of your system gets saved as a file on your drive. So, when you power on your PC again, Windows can easily reinstate. This process is common between both the Windows utilities.
Now, the main difference between Hibernate and Fast Startup is how the Windows system reinstates thereafter. When you turn on Windows 10 after putting into a Hibernate mode , the system runs all the last-opened services and apps during the startup.
In a Fast Startup -enabled mode, Windows 10 only runs the basic services . Unlike the Hibernate mode, Fast Startup doesn’t run unneeded services and third-party apps. As a result, your Windows 10 starts faster with Fast Startup than post-hibernation.
-
Fast Startup vs. UEFI Fast Boot (BIOS)
In Windows 10, the Fast Startup feature is also different from the Fast Boot feature. Some users must have accessed the UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) settings on their Windows 10 to enable or disable the Fast Boot option. Well, it is not the same as Fast Startup feature found in Power Options on Windows 10.
And, not just in Windows 10, you’ll find the Fast Boot feature in the BIOS of earlier Windows versions as well. So, the Fast Startup feature is relatively newer than the Fast Boot utility on Windows.
Then, some other differences in Fast Startup and Fast Boot include –
- Unlike Fast Startup, the Fast Boot utility skips certain POST stages
- Sometimes, enabling Fast Boot can stop you from accessing BIOS / UEFI settings ( unless you reset CMOS )
- The overall boot time reduced by Fast Startup is more significant than Fast Boot
- You can’t troubleshoot Fast Boot problems easily
- Fast Startup ensures high system stability
Also, for a fast Windows 10, disabling the Fast Startup is much safer and convenient than turning off the Fast Boot from UEFI settings.
Why Disable Fast Startup in Windows 10?
Speaking of disabling the Fast Startup feature, let’s learn more on why one should turn this tool off on their Windows 10 PC. There are more pros to enabling Fast Startup in Windows 10 than its cons. But, two specific downsides of this feature stack up well against its pros.
The foremost disadvantage of enabling Fast Startup in Windows 10 is your main hard drive getting locked . If you disable Fast Startup, Windows doesn’t lock up the C: drive during a system shutdown.
Turning off the Fast Startup feature gives you access to the primary partition of your hard drive. If the feature is enabled, you won’t be able to open files & documents on your C: drive.
It’s another major drawback for Windows 10 users who use Dual Boot on their computer. If your computer has two operating systems – Windows 10 and say Linux – then you may want to use Dual Boot often. But, when the Fast Startup feature in Windows 10 is enabled, you’ll be unable to access your hard drive after the Dual Boot .
Now, without the Fast Startup , Windows 10 shuts down legally . This is the second reason why disabling Windows 10 Fast Startup is good for your PC. When enabled, the Fast Startup feature doesn’t allow Windows 10 to configure some basic services and processes during a shutdown. So, your system is unable to configure newly-installed updates. Windows 10 doesn’t get time to apply recent changes to software packages when the Fast Startup is turned on.
There are more reasons that add up to why you should disable Fast Startup in Windows 10. Because, when you enable Fast Startup –
- your system doesn’t undergo a regular shutdown
- new system updates aren’t applied
- encrypted hard drives get automatically remounted after reboot
- encrypted disk, software face interference
- Windows 10 is unable to support Hibernate mode
If you can live with these issues, then go ahead and keep the Fast Startup feature enabled on your Windows 10. Once you experience these problems causing a drop in your computer’s performance, turning off the Fast Startup becomes your only option.
How to Disable Fast Startup in Windows 10?
So, let’s learn the different ways in which you can turn off Fast Startup in Windows 10.Now, you don’t need to explain the process of enabling Fast Startup in Windows 10. By default, the Fast Startup is enabled in every Windows 10 system.
Disabling the Fast Startup is a slightly different ballgame. There are some simple ways to follow, and some complicated methods.
According to several tech guides, one can disable Fast Startup in at least three effective and different ways.
Starting with the simplest way, you’ll disable the feature by un-checking it in its default settings window – the Power Options menu.
- Right-click on the Start menu icon
- Go to ‘ Power Options ’ from the context menu
- Click on ‘ Choose what the power button does ’
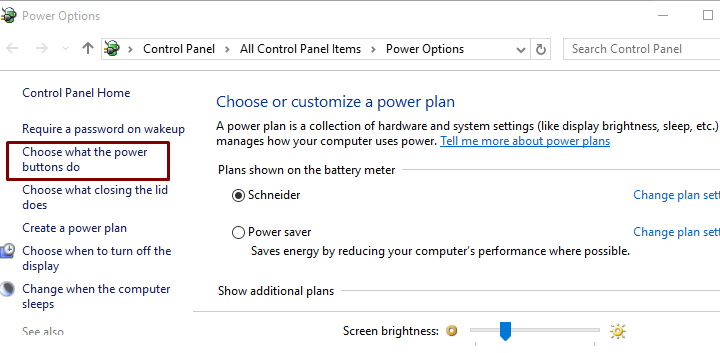
- Now, click on ‘ Change settings that are currently unavailable ’
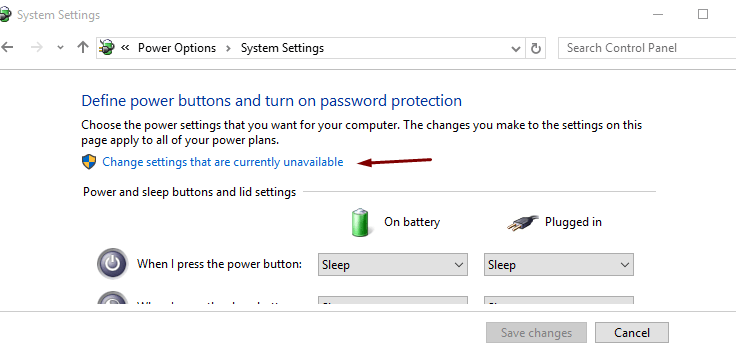
- Here, you’ll get an UAC prompt asking you to unlock the shutdown configurations; click on Yes
- In the System Settings window, browse to the Shutdown Settings section
- Under it, you’ll see the first setting – “ Turn on fast startup (recommended) ”
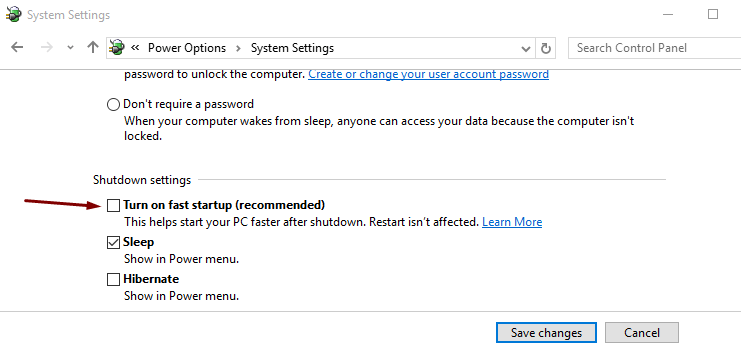
- Uncheck this option
- Click on Save changes
If you’ve disabled the hibernate mode on your Windows 10 system, you won’t see this option. To get it back,
- Go to search box and type ‘ cmd ’
- Right-click on Command Prompt and select ‘ Run as administrator ’
- Now, type the command-line – powercfg /hibernate on
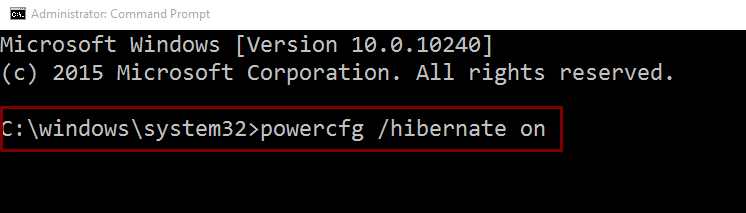
- Press the Enter key
Now, redo the steps and you’ll see the Fast Startup option in the System Settings window.
2. Registry Editor/BAT File
You can also force stop the Fast Startup feature in Windows 10. A registry edit helps you disable the utility permanently, and you won’t be able to enable it with the above route.
With the help of Registry Editor, you’ll change the value of the Fast Startup setting on Windows 10. To do this, you should know that the Windows Registry identifies Fast Startup as ‘ Hiberboot ’. The term fits well since Fast Startup is a hybrid state of hiber nation and boot ing up.
To disable Fast Startup with Registry Editor,
- Press ‘ Windows ’ key and tap ‘ R ’ key to open Run dialog
- Type “ regedit ” in the box and click on OK
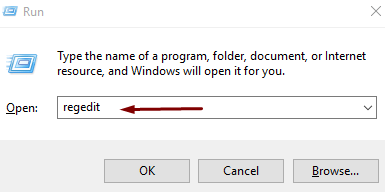
- Now, in the Registry Editor window, navigate to the following –
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
- \SYSTEM
- \CurrentControlSet
- \Control
- \Session Manager
- \Power
Here, you’ll see the DWORD – HiberbootEnabled . To turn off the Fast Startup, set the value of this DWORD as “0”.
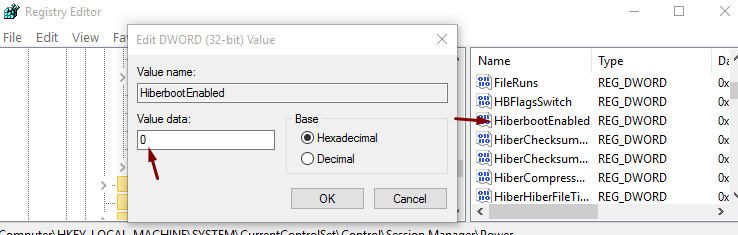
- Right-click on the entry and click on Modify
- Set the decimal value to “ 0 ”
- Click on OK to save the changes
- Now, close the registry editor
You may want to restart your PC to put the changes into effect. To get through with the registry edits in a quicker way, you can also run a batch (.bat) file .
You can download the .bat file here . It is a script file that disables the Fast Startup feature with the help a command-line interpreter.
- Save the file on your desktop
- Right-click on bat and select – Run as administrator
- You’ll see a UAC prompt, click on Yes
Now, running the BAT file takes only a moment. You’ll see the Command Prompt window flicker on your desktop for a second. That’s how the BAT file quickly applies the registry changes with Command Prompt. You can delete the downloaded .bat file later and restart your Windows 10 PC.
3. Disabling Hibernation
As discussed earlier, you won’t see the Fast Startup option when hibernation on your Windows 10 is disabled. So, does this mean that turning off hibernation disables Fast Startup on Windows 10?
Yes, it does work so. When you disable your system’s hibernate mode, you force remove the hiberfil.sys file. In the absence of this file, Windows is unable to run Fast Startup process. So, technically, the feature gets disabled.
To disable the hibernate mode,
- Go to the search box and type ‘ cmd ’
- Right-click on Command Prompt
- Select – Run as administrator
- Now, type the command-line: powercfg –h off
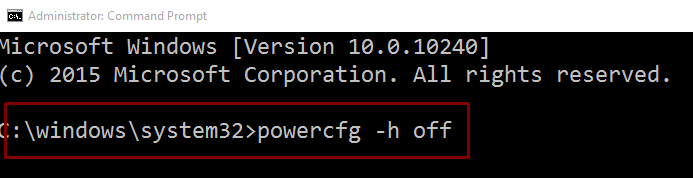
- Press the Enter key
Now, you won’t be able to put Windows 10 in hibernate mode. And, consequentially, the Fast Startup feature gets disabled. Owing to the downsides of hibernating , several Windows 10 users may resort to this method as a way to disable Fast Startup.
Troubleshooting Fast Startup in Windows 10
Fast Startup is a feature enabled by default in Windows 10. To further disappointment, this “recommended” setting gives rise to other problems for your operating system.
You can troubleshoot problems caused by Fast Startup by simply disabling the feature. But, for some issues, disabling Fast Startup won’t get your Windows 10 fixed.
After installing updates on Windows 10, you’re asked to reboot PC. This way, the operating system reconfigures itself with the new updates.
With Fast Startup enabled, Windows is unable to successfully install the updates. Some patch installations in the new updates require a normal shutdown, which the Fast Startup skips over.
You can disable the Fast Startup and restart the computer to troubleshoot this issue. It is also advised to turn off this feature before installing updates. Then, you can execute a full shutdown to complete the system reconfigurations.
If you have enabled Fast Startup on Windows 10 or Windows 8.1, you may have trouble shutting down your PC. It’s happened that the shutdown process fails when the Fast Startup feature is enabled.
Windows users weren’t able to hibernate or shut their PCs down and were reverted back to the Windows Lock screen. The enabled feature doesn’t initialize the system memory dump configuration. As a result, the driver doesn’t get loaded, bringing back Windows to its login screen.
In such an event, you don’t need to force shutdown or hybrid hibernate your Windows 10. You can run the Shutdown.exe file manually and fix the issue.
Run the Command Prompt program as administrator (shown earlier) and type “ Shutdown /s /t 0 ”. Execute this command-line by pressing the Enter key. You can also use the optional parameter – hybrid shutdown. The command-line for that is “ Shutdown /s /hybrid /t 0 ”.
Let us know how you dealt with disabling Fast Startup in Windows 10. Please send your comments to help us know more on issues caused by Fast Startup in Windows .
Also Read: